数据结构Map 总结
Map
这里只对常用Map集合进行分析
HashMap
hashmap 底层是entry的一个数组 每个数组内又是一个entry维护的单向链表(至于为何还需要一个单向链表后续解释) 每个entry 存储 k v hash值 因为插入的位置是 hash值与table长度取模 所以无序 为什么entry数组内还要维护一个单向链表呢? 哈希冲突哈希冲突
通过哈希函数得出的实际存储地址相同怎么办?也就是说,当我们对某个元素进行哈希运算,得到一个存储地址,然后要进行插入的时候,发现已经被其他元素占用了, 其实这就是所谓的哈希冲突,也叫哈希碰撞。前面我们提到过,哈希函数的设计至关重要,好的哈希函数会尽可能地保证 计算简单和散列地址分布均匀,但是, 我们需要清楚的是,数组是一块连续的固定长度的内存空间,再好的哈希函数也不能保证得到的存储地址绝对不发生冲突。 那么哈希冲突如何解决呢?哈希冲突的解决方案有多种:开放定址法(发生冲突,继续寻找下一块未被占用的存储地址), 再散列函数法,链地址法,而HashMap即是采用了链地址法,也就是数组+链表的方式,
简单来说就是因为两个key的hash值相同占用了数组同一位置 所以将数组元素转换为单向链表加入原 元素后面
二、HashMap实现原理
HashMap 结构图
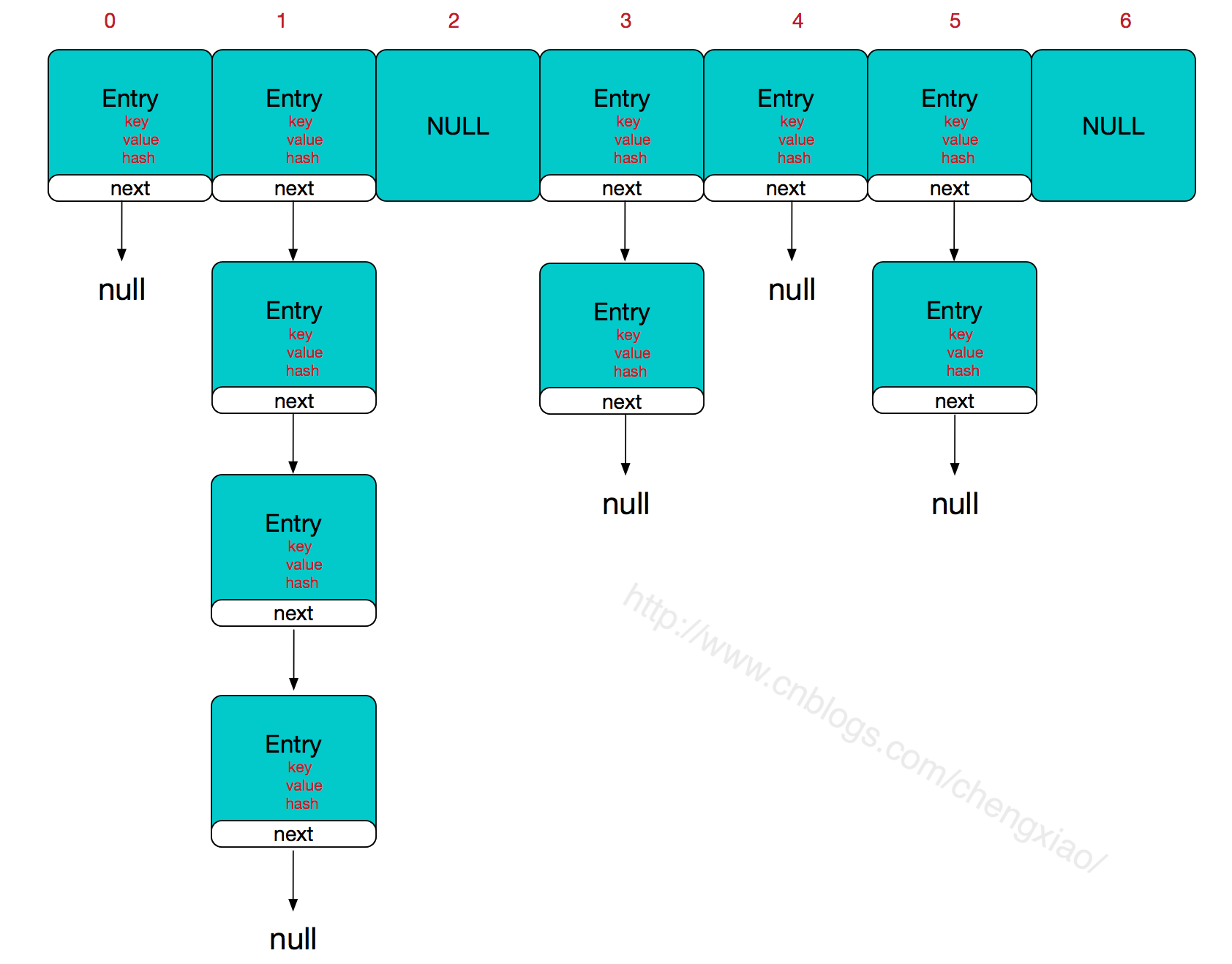
简单来说,HashMap由数组+链表组成的,数组是HashMap的主体,链表则是主要为了解决哈希冲突而存在的,如果定位到的数组位置不含链表(当前entry的next指向null), 那么对于查找,添加等操作很快,仅需一次寻址即可;如果定位到的数组包含链表,对于添加操作,其时间复杂度为O(n),首先遍历链表,存在即覆盖,否则新增; 对于查找操作来讲,仍需遍历链表,然后通过key对象的equals方法逐一比对查找。所以,性能考虑,HashMap中的链表出现越少,性能才会越好。
HashMap的主干是一个Entry数组。Entry是HashMap的基本组成单元,每一个Entry包含一个key-value键值对。
//HashMap的主干数组,可以看到就是一个Entry数组,初始值为空数组{},主干数组的长度一定是2的次幂,至于为什么这么做,后面会有详细分析。
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
Entry是HashMap中的一个静态内部类。代码如下
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;//存储指向下一个Entry的引用,单链表结构
int hash;//对key的hashcode值进行hash运算后得到的值,存储在Entry,避免重复计算
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
HashMap 方法使用及源码解析
put 首先查询原table内是否有该key 如果有则覆盖 没有则添加Entry
public V put(K key, V value) {
//如果table数组为空数组{},进行数组填充(为table分配实际内存空间),入参为threshold,此时threshold为initialCapacity 默认是1<<4(24=16)
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//如果key为null,存储位置为table[0]或table[0]的冲突链上
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);//对key的hashcode进一步计算,确保散列均匀
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);//获取在table中的实际位置
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
//如果该对应数据已存在,执行覆盖操作。用新value替换旧value,并返回旧value
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;//保证并发访问时,若HashMap内部结构发生变化,快速响应失败
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);//新增一个entry
return null;
}
/**
* Returns index for hash code h. 获取table内hash值的元素位置 h & (length-1)
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
get 根据hash值查找entry所在table内位置 遍历entry链表 直到hash相同,且key equals相同 返回元素
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
/**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);//计算keyhash值
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];//根据hash值查找entry所在table内位置
e != null;
e = e.next) {//遍历entry链表 直到hash相同,且key equals相同 返回元素
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
这里因为hashMap内使用了table的一个数组,那如何解决数组的扩容问题 以及扩容后 hash值对应index的问题呢? 先来看看inflateTable这个方法
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);//capacity一定是2的次幂
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);//此处为threshold赋值,取capacity*loadFactor和MAXIMUM_CAPACITY+1的最小值,capaticy一定不会超过MAXIMUM_CAPACITY,除非loadFactor大于1
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
inflateTable这个方法用于为主干数组table在内存中分配存储空间,通过roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize)可以确保capacity为大于或等于toSize的最接近toSize的二次幂, 比如toSize=13,则capacity=16;to_size=16,capacity=16;to_size=17,capacity=32.
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) {
// assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative";
return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
: (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1;
}
roundUpToPowerOf2中的这段处理使得数组长度一定为2的次幂,Integer.highestOneBit是用来获取最左边的bit(其他bit位为0)所代表的数值.
//对key的hashcode进一步进行计算以及二进制位的调整等来保证最终获取的存储位置尽量分布均匀
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
/**
* 返回数组下标
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);//当size超过临界阈值threshold,并且即将发生哈希冲突时进行扩容
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
通过以上代码能够得知,当发生哈希冲突并且size大于阈值的时候,需要进行数组扩容,扩容时,需要新建一个长度为之前数组2倍的新的数组, 然后将当前的Entry数组中的元素全部传输过去,扩容后的新数组长度为之前的2倍,所以扩容相对来说是个耗资源的操作。
注意:重写equals方法需同时重写hashCode方法 尽管我们在进行get和put操作的时候,使用的key从逻辑上讲是等值的(通过equals比较是相等的),但由于没有重写hashCode方法,所以put操作时, key(hashcode1)-->hash-->indexFor-->最终索引位置 ,而通过key取出value的时候 key(hashcode1)-->hash-->indexFor-->最终索引位置,由于hashcode1不等于hashcode2, 导致没有定位到一个数组位置而返回逻辑上错误的值null(也有可能碰巧定位到一个数组位置,但是也会判断其entry的hash值是否相等,上面get方法中有提到。)
所以,在重写equals的方法的时候,必须注意重写hashCode方法,同时还要保证通过equals判断相等的两个对象,调用hashCode方法要返回同样的整数值。 而如果equals判断不相等的两个对象,其hashCode可以相同(只不过会发生哈希冲突,应尽量避免)。
LinkedHashMap 继承自hashMap 在hashMap的基础上 增加为维护一个双向指针的操作 所以达到元素有序的效果 这里源码方法就不解析了 基本就是增删元素 维护指针的操作
/**
* The head of the doubly linked list.
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> header;
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
TreeMap java红黑树数据结构实现
由于之前讲过红黑树相关内容这里不做具体讲解有兴趣可以看之前的文章 这将源码与之前讲解一一对应
插入put(K key, V value) 插入红黑树元素
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) { //如果为空直接当作root加入
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {//-----比较元素compareTo 寻找元素插入位置
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);//插入元素后进入fixAfterInsertion 插入调整
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
//插入调整函数
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
x.color = RED;//首先元素插入必为红色 否则会改变黑高违反特性
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {//如果parent为黑色 blackover 结束无须调整
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); //case 1 Y 为红色,X可以为左孩子或者右孩子:P,Y染黑 G染红 X回溯至G
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { //case 2 Y为黑色 X为右孩子:左旋P X指向P 转化为case3
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); //case3.Y为黑色,X为左孩子:P染黑 G染红 右旋G 结束
}
} else { // X 父亲为右孩子 前面三个case 镜像
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
root.color = BLACK;
}
红黑树删除元素 fixAfterDeletion 删除调整
删除调整(fixAfterDeletion) case1.兄弟节点S为红色 兄弟节点染黑 父节点染红 左旋P case2.兄弟节点S为黑色 黑LN,黑RN ; S染红 X回溯P case3.兄弟节点S为黑色 红LN 黑RN ; LN染黑 S染红 ,右旋S case4.黑S兄弟节点 LN随意,红RN ; S变P颜色 P和RN染黑,左旋P
/**
* Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree.
*/
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
/** From CLR */
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else { // symmetric
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}
